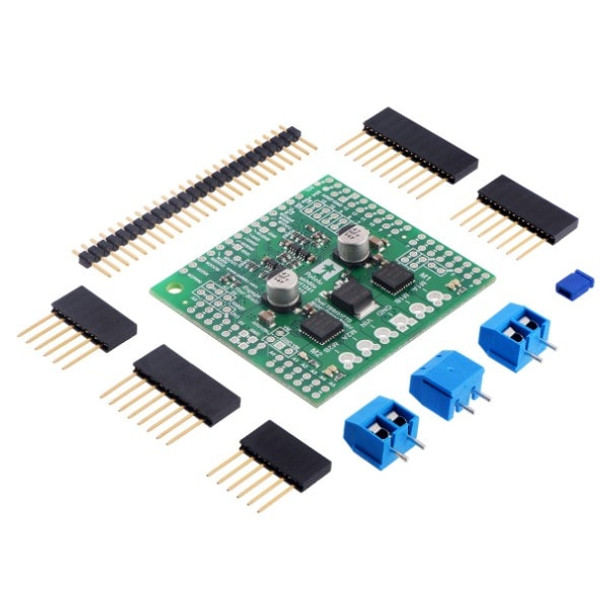
Description
Dual TB9051FTG Motor Driver Shield for Arduino - Pololu 2520
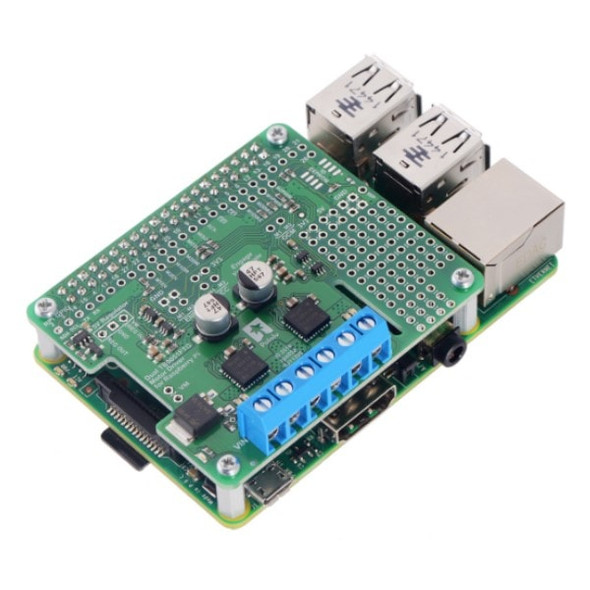
This motor driver shield and its corresponding Arduino library make it easy to control two bidirectional, brushed DC motors with an Arduino or compatible board. The board features a pair of Toshiba TB9051FTG motor drivers, which operate from 4.5 to 28 V and can deliver up to 2.6 A per channel continuously, and includes current sense circuitry, reverse battery protection, and logic gates to reduce the required number of I/O pins. The drivers automatically limit the peak current to around 5 A, which they can deliver for a few seconds in typical applications before the thermal protection activates.
This versatile motor driver is intended for a wide range of users, from beginners who just want a plug-and-play motor control solution for their Arduinos (and are okay with a little soldering) to more advanced users. The Arduino pin mappings can all be customized if the defaults are not convenient, and the simplified TB9051FTG control lines are broken out along the left side of the board, providing a convenient interface point for other microcontroller boards. This versatility, along with an option to power the Arduino from the shield, either directly or through an added regulator, sets this board apart from similar competing motor shields.
The board ships fully populated with its SMD components, including the two TB9051 ICs, as shown in the left picture above; stackable Arduino headers and terminal blocks for connecting motors and motor power are included but are not soldered in.
General Specifications:
| Motor driver: | TB9051FTG |
|---|---|
| Motor channels: | 2 |
| Minimum operating voltage: | 4.5 V 1 |
| Maximum operating voltage: | 28 V 2 |
| Continuous output current per channel: | 2.6 A 3 |
| Peak output current per channel: | 5 A |
| Current sense: | 0.5 V/A |
| Maximum PWM frequency: | 20 kHz |
| Reverse voltage protection?: | Y 4 |
Notes:
-
- Operation from 4.5 V to 8 V reduces maximum current output.
- Transient operation (< 500 ms) up to 40 V.
- Typical results at room temperature with VIN > 8 V and both channels running 90% duty cycle. Operation from 4.5 V to 8 V reduces maximum current output.
- On motor voltage only; logic voltage does not have reverse protection.
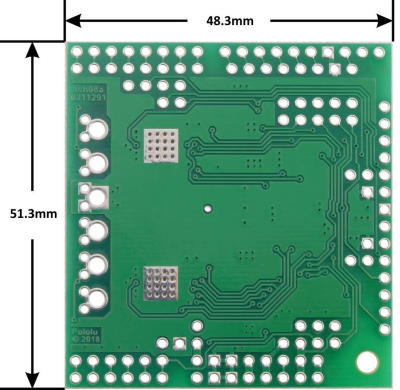
Dimensions:
- Size: 48.3 x 51.3 x 7.7 mm (1.9" x 2.02" x 0.3")
- Weight: 11 g
Included Hardware:
This motor driver board ships with all of the surface-mount parts populated. However, soldering is required for assembly of the included through-hole parts. The following through-hole parts are included:
The terminal blocks can be soldered into the larger holes to allow for convenient temporary connections of unterminated power and motor wires or you can break off a 12×1 section of the 0.1″ header strip and solder it into the smaller through-holes that border these larger holes. You can also solder wires directly to the board:
When not using this board as an Arduino shield, you can solder the pieces of the 0.1″ header to the logic connections along the left side of the board to enable use with custom cables or solderless breadboards, or you can solder wires directly to the board for more compact installations. Note that motor and motor power connections should not be made through a breadboard.
Schematic Diagram:
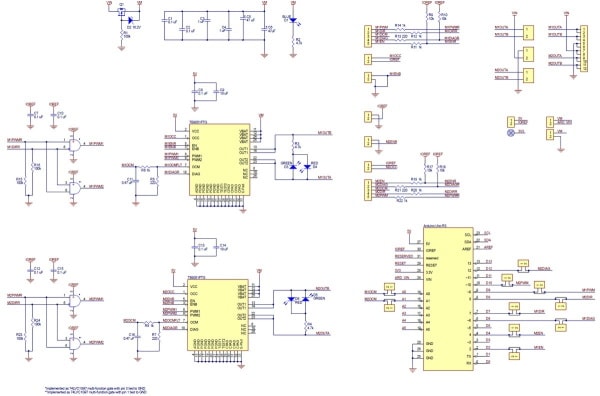
Current Sensing:
The current monitor outputs, M1OCM and M2OCM, provide an analogue current-sense feedback voltage of approximately 500 mV per A. By default, these outputs are connected to Arduino analogue inputs A0 and A1, respectively. Note that each of these outputs is only active while the corresponding H-bridge is driving; it is inactive (low) when the driver is braking or the motor outputs are high impedance (floating). If the driver is braking, current will continue to circulate through the motor, but the voltage on the OCM pin will not accurately reflect the motor current. Please note that like most motor drivers with integrated current sense, the actual sensitivity can vary significantly from unit to unit, and accuracy can be especially poor at low currents (see the TB9051FTG datasheet in the Documents section for more information).
Real-World Power Dissipation Considerations:
The TB9051FTG will start chopping its output current at a typical threshold of 6.5 A. However, the chip by itself will typically overheat at lower currents. In our tests, we found that the chip was able to deliver 5 A for only a few seconds before the chip’s thermal protection kicked in; a continuous current of about 2.6 A per channel was sustainable for many minutes without triggering thermal current limiting or an over-temperature shutdown. The actual current you can deliver will depend on how well you can keep the motor driver cool. The shield’s printed circuit board is designed to help with this by drawing heat out of the motor driver chip. PWMing the motor will introduce additional heating proportional to the frequency.
Unlike typical H-Bridges, the TB9051FTG has a feature that allows it to gracefully reduce the maximum current limit when the chip temperature approaches its limit. This means that if you push the chip close to its limit, you will see less power to the motor, but it might allow you to avoid a complete shutdown.
This product can get hot enough to burn you long before the chip overheats. Take care when handling this product and other components connected to it.
Documents:
- Dimension Drawing for the Dual TB9051FTG Motor Driver Shield (pdf)
- Schematic Diagram for the Dual TB9051FTG Motor Driver Shield (pdf)
- Datasheet for the TB9051FTG H-Bridge (pdf)
- 3D Model of the Dual TB9051FTG Motor Driver Shield (1.34MB zip)
- Drill Guide for the Dual TB9051FTG Motor Driver Shield (6.94k zip)